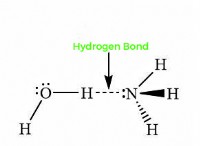
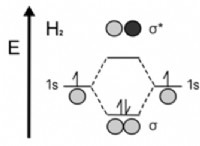
* 높은 전기 음성 : Halogens have very high electronegativity values, meaning they have a strong attraction for electrons. This makes them highly reactive, as they readily gain electrons to form negative ions (halide ions).
* Small atomic size: Halogens have relatively small atomic radii. This results in a strong attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons, making it easier to gain an electron to achieve a stable octet.
* Seven valence electrons: Halogens have seven electrons in their outermost shell, making them one electron short of a stable octet. This strong drive to achieve a stable configuration is what makes them highly reactive.
* Strong oxidizing power: Halogens are strong oxidizing agents, readily accepting electrons from other elements. This further contributes to their high reactivity.
In summary, the combination of high electronegativity, small atomic size, seven valence electrons, and strong oxidizing power makes halogens the most reactive of the nonmetal elements. They readily form ionic bonds with metals and covalent bonds with other nonmetals, leading to a wide range of chemical reactions and compounds.